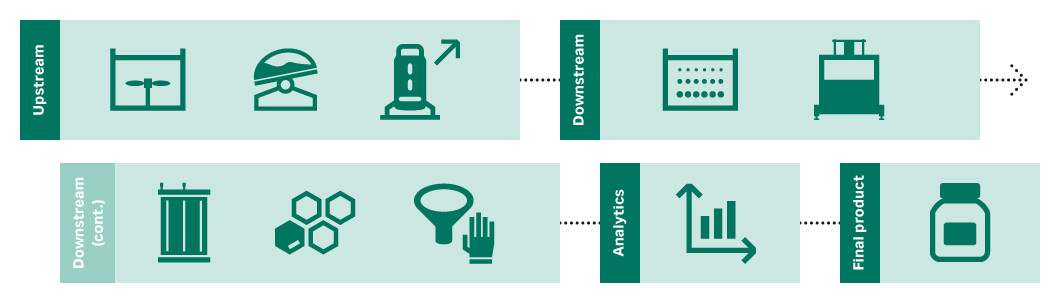
The objective of the buffer and media step is to hydrate the dry powders. Consider ways to reduce variability, maintain consistency, and maximize reproducibility. Weigh the options between doing hydration in-house or outsourcing the prepared liquids.
Learn more:
• Buffer and media management
• Cell culture solutions
In the cell culture seed train step you’ll generate cell concentrations at maximum cell viability, with high productivity, titers and product quality. That can be used to inoculate production bioreactors.
Learn more:
• Basics of process development
• Cell culture media development service
• Single-use-bioreactors
In the upstream scale-up step, you’ll increase the scale for manufacturing to achieve a consistent and cost-effective process. It’s important to control your critical process parameters (CPPs) in the predetermined ranges to ensure consistent product quality.
Learn more:
• Fed-batch scale-up
The objective of the clarification step is to remove cells. Choose the right filter media and sizing, and make sure that your clarification system is scalable. Consider single-use, closed systems to reduce steps and handling.
The capture step isolates the target product and reduces host cell protein (HCP). Affinity chromatography is widely used, because purities are high ( > 95% for some protein A resins). Consider prepacked columns to reduce changeover time and Fibro chromatography for multiproduct facilities.
Learn more:
• Basics of process development
• Downstream scale-up and tech transfer
• Fast mAb purification
The polishing steps are designed to remove product and process impurities, including viral clearance. HCP, leached ligand, DNA, viruses, aggregates, and other antibody forms must be removed to acceptable levels without excess product loss.
Learn more:
• Basics of process development
• Polishing chromatography
During formulation, the objective is to get the target molecule into a suitable buffer with high recovery. Select the right type and sizing of filter media and equipment to maximize recovery. Manage the risk of contamination with single-use, closed processing.
Learn more:
• Tangential flow filtration
The sterile filtration step maintains the low microbial bioburden to required levels. Consider how to maximize recovery and ensure integrity, both pre- and post-use. Perform filter studies to choose the right filter media and sizing. Manage the contamination risk with single-use, closed processing.
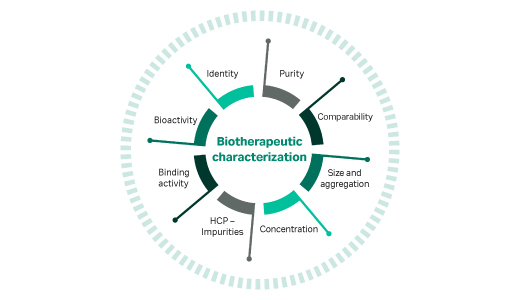
You will use multiple assays to analyze and measure your product’s purity, potency, strength, and identity. Consider assay specificity and sensitivity, and think about automating for speed and control. Best practice is to use orthogonal (additional) assays to confirm results.
Learn more:
• Visit bioanalytics resource hub
After formulation and QC, the bulk drug substance is stored in bottles or bags. It may be put into vials in a fill/finish step. If it will be cryopreserved at the bulk stage, consider controlled-rate freezing and thawing to avoid precipitation and loss of yield.
Learn more:
• Aseptic filling